SunForce™ is a highly functional material with unprecedented design possibilities.

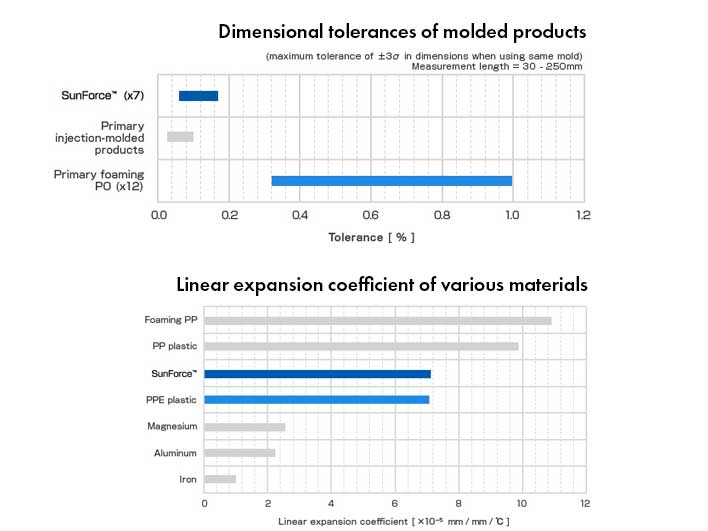
Dimensional Errors Of Molded Products
The dimensional tolerance (and dimensional error) refers to the variation in the dimensions of the molded product. General foam-molded products used in shock absorbing applications etc. exhibit large shrinkage and expansion during fabrication, with consequently large dimensional tolerances.
Due to its superior dimensional accuracy, SunForce can be used with confidence in structures and chassis applications, that do not allow dimensional tolerances.


Coefficient Of Linear Expansion
The linear expansion coefficient refers to the change in the dimensions of the material with temperature. The greater the value, the greater the dimensional change due to temperature. Although the numerical value for plastic is greater than for metal, SunForce assumes the characteristics of PPE plastic with its low coefficient of linear expansion in comparison with other plastics, and the effects of temperature are relatively small.
Low Warpage And Reduced Sinkage In Mold
One of the major features of foam molding. SunForce employs a method in which the mold is filled with beads which are then expanded and simultaneously fused with the heat from steam. This process differs from injection molding in which plastic is poured into a mold at high temperature and high pressure, and is characterized by less warpage and sinkage even when the product incorporates large variation in wall thickness. This allows for freedom in design so that, for example, uniform wall thicknesses are not required.
Application Areas
SunForce™ BE - Automotive Application
Automotive industry (exterior and interior parts, structural battery parts)
Public transportation
(airplane components, train components, railway infrastructure, electrical parts, seat parts)


Other industries
Other industries (E-wave applications)